Theories
- History of Learning Theories
- Learning Theories in Practice
- Behaviorism
- Humanism
- Cognitivism
- Constructivism
History of Learning Theories
Generally, learning theories develop explanation, hypotheses and statement about how people learn, which is defined as a process that involves acquiring and modifying knowledge, skills, strategies, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors (Schunk, 2012).
There are many systems of learning theories, and taken together, researchers have distinguished the major concepts and theories of learning into behaviorism, humanism, cognitivism, and constructivism (cognitive constructivism and social constructivism) based on historical development in changes of understanding.These learning theories are associated with different instructional models and approaches (see Instructional Approaches and Classroom Strategies).
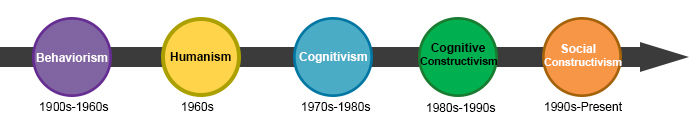
- Positive Reinforcement
- Rewards & Punishment
- Drills & Practice
- Experiential Learning
- Self-esteem
- Teacher-Student Relationship
- Advance Organizers
- Multimedia Learning
- Variation Theory
- Metacognition & Self-Regulated Learning
- Reading to Learn
- Problem-Based Learning
- Project-Based Learning
- Arguing to Learn
- Peer Learning
- Productive Failure
- Web-based Scientific Inquiry
- Concept Mapping
- Inquiry-Based Learning
- Accountable Talk
- Situated & Experiential Learning
- Collaborative Inquiry
- Learning Communities
- Knowledge Building
- Informal Learning
References
- Schunk, D. H. (2012) Learning theories: An educational perspective. New York, NY, England: Macmillan Publishing Co, Inc.